Breaking the Bottleneck | Issue 32
[11/20/2023] MIT 3D Printer, Battery Vision, Molex Reliability Survey, Space X & Andre 3000
Breaking the Bottleneck is a weekly manufacturing technology newsletter with perspectives, interviews, news, funding announcements, and a startup database. For a discrete and continuous manufacturing market map click the link here!
Content I Enjoyed This Week 🏭🗞️🔬
News:
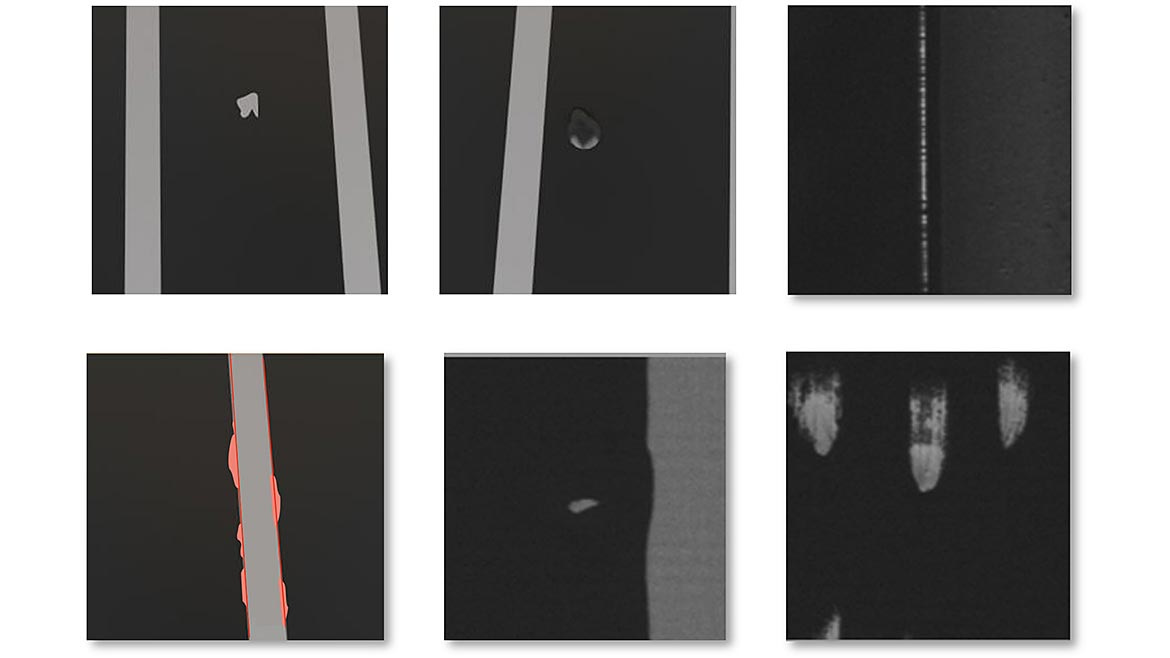
This 3D Printer Can Watch Itself Fabricate Objects [MIT News]
Engineers at MIT, the MIT spinout Inkbit, and ETH Zurich have developed a 3D inkjet printing system that utilizes computer vision for real-time adjustments in material deposition. Unlike traditional 3D printers that use mechanical parts to smooth resin, this contactless system scans the printing surface and adjusts the amount of resin each nozzle deposits. It works with a broader range of materials, including slower-curing options with improved properties, such as greater elasticity, durability, or longevity. The researchers demonstrated the technology by creating a 3D-printed robotic gripper shaped like a human hand. The new technology offers precise control over material deposition and opens up possibilities for using diverse materials in 3D printing.
Cadence and Autodesk Collaborate on Smart Product Design [Cadence]
Cadence Design Systems, Inc. has announced a collaboration with Autodesk to accelerate intelligent system design using Autodesk Fusion and Cadence PCB solutions. The integration facilitates seamless bi-directional communication between PCB designers and mechanical engineers, addressing challenges in manual design data methods that often lead to errors, re-work, and delays. The partnership aims to enhance collaboration between electronic and mechanical engineering, allowing efficient co-design and enabling companies to leverage cloud-based mechanical design, generative AI/ML PCB design, and multiphysics analysis for power, thermal, and electromagnetics. The joint solution supports Cadence's Intelligent System Design strategy.
Cracking The Code on Flow Battery Tech? [Canary Media]
CMBlu, a German flow-battery startup, recently secured a significant investment of 100 million euros from European construction services firm Strabag. Unlike many flow-battery competitors, CMBlu employs a unique approach by integrating solid components with liquid electrolytes, claiming improved energy storage efficiency and avoiding controversial minerals used in mainstream clean-energy technologies. The company's technology, based on organic components, allows for the production and recycling of a rechargeable polymer, eliminating the need for traditional metals found in batteries. This approach has attracted contracts with U.S. and European utilities, demonstrating commercial viability. CMBlu plans to construct an automated pilot factory in Germany and expand to larger-scale facilities in the U.S. by 2025.
Machine Vision for Battery Production [Quality]
Machine vision plays a crucial role in the intricate and highly precise process of lithium-ion battery production, contributing to the overall value of the battery production chain, which McKinsey predicts will exceed $400 billion by 2030. The value generated from cell production alone constitutes approximately 30% of this total. The technology aids in defect inspection, object recognition, and decision-making across multiple steps in the battery production process. In electrode manufacturing, machine vision is utilized to ensure the quality of coated electrode sheets, checking for defects, impurities, and dimensional accuracy. The high-speed nature of the coating process, reaching speeds of up to 80 meters per minute, requires robust detection and classification of even the smallest defects. During the separation steps, the coated electrode foil is divided into narrower strips or individual sheets. Machine vision not only verifies dimensions but also detects issues such as burrs, impurities, and unclean cuts. In cell assembly, the subsequent production step involves stacking electrode foils and a separator before insertion into the battery housing. Machine vision software inspects weld seams, using artificial intelligence (AI) approaches to detect a variety of defects that may occur during the welding process. Finally, end-of-line tests before shipping involve visual inspections using machine vision to quickly identify and reject damaged battery cells. The technology can recognize deformities, deviations from specified dimensions, surface damage, unreadable codes, and foreign bodies.
Robotics Q&A with TRI’s Max Bajracharya and Russ Tedrake [TechCrunch]
In a recent interview, Russ Tedrake and Max Bajracharya discussed a variety of robotics topics :
Generative AI - More work is needed to understand how to ground image and language knowledge in the types of physical intelligence required to make robots truly useful
Humanoid Robots - Bajracharya mentioned that while robots assisting people need to fit into human-designed environments, they don't necessarily have to adopt a humanoid form. The key is for robots to be compact, safe, and capable of performing human-like tasks.
General Purpose Robots - Tedrake expressed optimism about steady progress in moving from niche robots to more general-purpose ones. While the timeline is uncertain, increasing autonomy and broader capabilities are expected to benefit various industries, including flexible automation, high-mix manufacturing, and point-of-service robots.
Overlooked Trends - Tedrake emphasized the importance of the quiet revolution in simulation within the robotics community. He highlighted the significant progress made in training and testing computer vision systems in simulation, challenging the skepticism that existed only a few years ago.
GM Buys Tesla’s Sand 3D Printing Provider for Gigacasting [3D Print.com]
General Motors (GM) has strategically acquired Tooling & Equipment International (TEI), for around $100 million and is part of GM's strategy to strengthen its position in the competitive EV market and own a key player who developed gigacasting technology for Tesla. TEI's expertise in sand casting techniques, particularly 3D-printed sand molds, has played a crucial role in Tesla's gigacasting innovations. GM's acquisition is significant for the automotive industry, particularly in the electric vehicle (EV) market. Tesla's gigacasting advancements and the use of 3D-printed sand molds have enabled faster and more cost-effective manufacturing of large components for electric vehicles. GM's acquisition positions the company to better compete with Tesla in the rapidly evolving EV market, where gigacasting is becoming a key factor for manufacturing efficiency and cost reduction.
Research:
The Chip Industry’s Reshoring Revolution [RBC]
Various countries, recognizing the strategic importance of semiconductor manufacturing, are making substantial investments to enhance their capabilities. In the U.S., the CHIPS and Science Act was introduced, allocating $52 billion in subsidies and substantial investments from companies like TSMC and Samsung in building fabs in the U.S. China has been actively working to reduce dependencies on foreign-made chips since 2014, investing $50 billion initially, with plans to allocate $100 billion to $150 billion. Despite progress, China has not achieved full self-reliance, and it remains a significant importer of semiconductors. In Europe, the European Chips Act aims to double the EU's share of the global semiconductor market to 20% by the end of the decade. TSMC, in collaboration with European companies, has announced plans to construct a €10 billion ($10.7 billion) plant in Germany.
Reliability and Hardware Design Survey [Molex]
Molex surveyed over 750 system architects and design engineers across the globe to better understand today’s challenges to reliability and what the future may bring. Below are some insights from the report:
A nearly unanimous 98% of respondents report challenges designing for reliability, with time for testing (42%) topping the list.
Only 33% of respondents use data-based models to help evaluate design tradeoffs. Most rely on a combination of predetermined design priorities and judgment calls
91% of those surveyed agree that reliable products can’t be built without trusted and proven suppliers. Supplier expertise and engagement are even more critical when considering that 74% of engineers agree that reliability may be at risk due to shortening design cycles.
The vast majority of respondents (96%) have concerns about overall reliability in electronics products, with increasing complexity of devices (53%) and growing customer expectations of reduced costs (49%) topping the chart.
Podcasts:
Albert Einstein [In Our Time: Science]
Recycling the World’s Batteries [TED - Emma Nehrenheim]
Chart of the Week:
[Economist] The real realignment of global value chains
Manufacturing Deals
Divergent Technologies - A company developing a Divergent Adaptive Production System (DAPS), intended to act as an end-to-end system-level replacement for traditional design, manufacturing, and assembly solutions
$230 million [Series D] - Led by Hexagon AG
Keychain - A company building a platform to help brands and retailers find manufacturing partners
$18 million [Seed] - Led by Lightspeed Venture Partners and joined by Box Group, Afore Capital and SV Angel
Weekly Planned Downtime
SpaceX Starship Second Try
André 3000 Talks His New Album and Life After Outkast




Cam on ban da chia se bai viet nay! Bai viet rat hay va bo ich doi voi toi. Welcome to my website at https://nasami.vn/coconut-water/