Breaking the Bottleneck | Issue 66
[11/25/2024] AI Chip Design, Deloitte's 2025 Manufacturing Outlook, & Cobot Announcement
Breaking the Bottleneck is a weekly manufacturing technology newsletter with perspectives, interviews, news, funding announcements, manufacturing market maps, and a startup database!
💥 If you are building, operating, or investing in manufacturing, hardware, or robots, please reach out. My email is aditya@schematicventures.com – I’d love to connect!
🏭 If you were forwarded this and found it interesting, please sign up!
Content I Enjoyed Last Week 🏭🗞️🔬 📚
News:
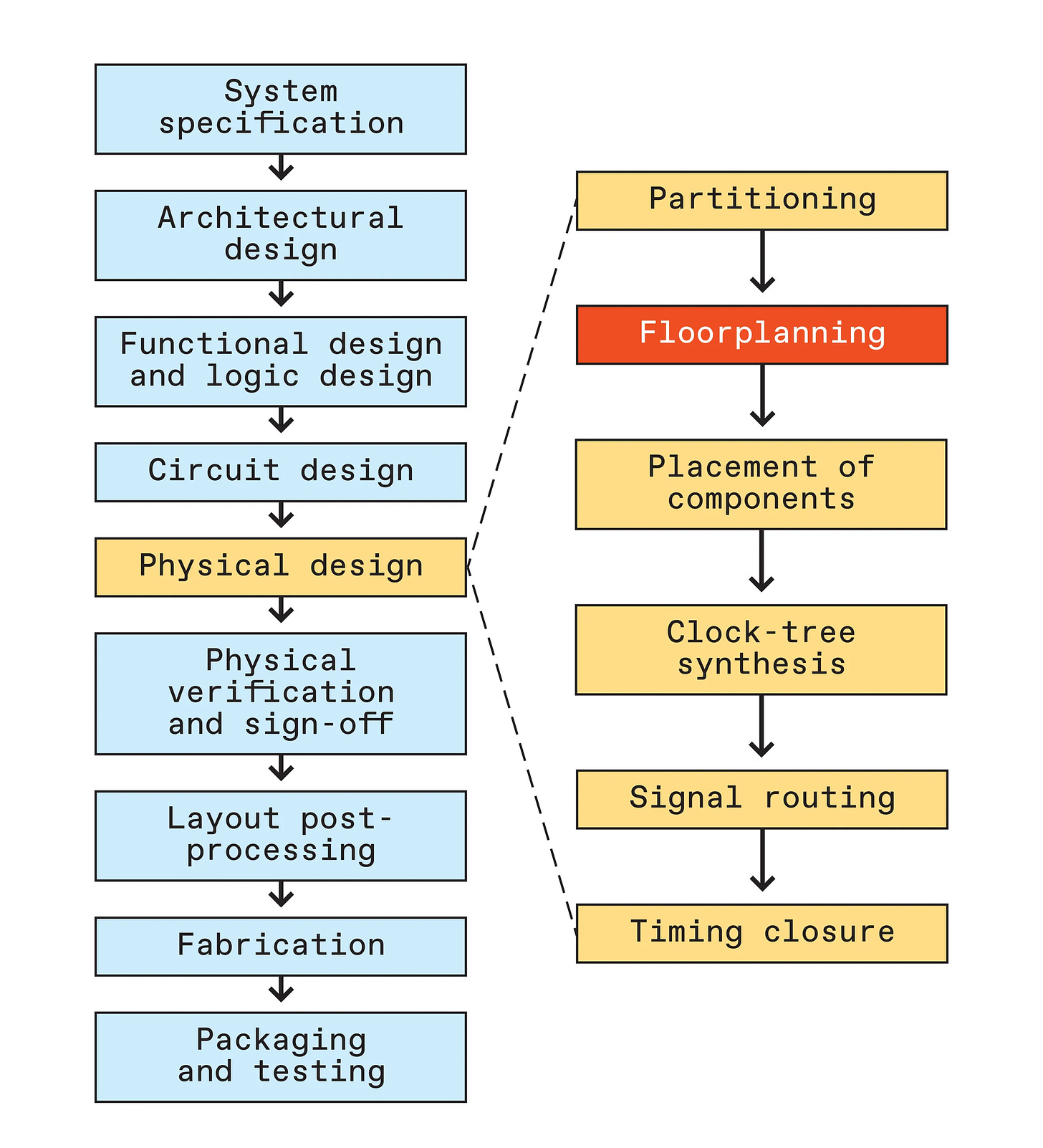
AI Alone Isn’t Ready for Chip Design [IEEE Spectrum]
Modern chip design, involving hundreds of billions of transistors, faces significant challenges due to increasing complexity and stringent performance, power, and cost constraints. A critical bottleneck lies in the physical design stage, particularly floorplanning, which arranges functional blocks like CPU cores and memory to optimize wire length, chip area, and power efficiency. While machine learning (ML) approaches have shown potential for accelerating chip design, they often falter under the hard constraints inherent to floorplanning. For instance, Intel AI Lab’s ML models using graph neural networks and transformer-based algorithms struggled with sequential block placement, resulting in suboptimal layouts and impractical exploration requirements for reinforcement learning. While more robust, traditional optimization techniques like simulated annealing (SA) also encountered limitations in handling these constraints effectively. To address this, the team developed constraints-aware simulated annealing (CA-SA), combining an SA module for optimizing wire length and area with a repair module to address constraint violations. This innovation, implemented in the open-source tool Parsac, achieved breakthroughs in solving commercial-scale floorplanning problems with approximately 100 blocks in under 15 minutes, outperforming existing methods. Recognizing AI’s strengths in pattern recognition but limitations in combinatorial optimization, the team advocates for hybrid approaches where AI models guide traditional algorithms to accelerate convergence and avoid suboptimal solutions. To foster further innovation, they released two open-source datasets, FloorSet-Lite and FloorSet-Prime, featuring millions of layouts reflecting modern system-on-chip (SoC) designs. These advancements demonstrate the potential of blending AI and traditional techniques to enable faster, more efficient chip designs, paving the way for next-generation, power-efficient processors.
Mixed-Model Lines Enable Multiple Power Train Configurations [Assembly]
Automakers globally are confronting unprecedented production challenges as they strive to operate flexible assembly lines capable of producing both gasoline-powered and battery-powered vehicles simultaneously while maintaining productivity and quality standards. Assembling different powertrain variants demands efficient use of floor space, streamlined parts management, and cross-trained operators. Mixed-model assembly introduces high variability, posing significant challenges for organizations. Implementing mixed-model assembly lines requires high process standardization within existing plant layouts, significant capital investment, and the upskilling of the workforce to handle a diverse product mix and ensure consistent product data across CRM, ERP, and MES systems. Several automakers are investing in flexible factories to address these challenges:
Stellantis is investing over $406 million in Michigan facilities to support a multi-energy strategy. Its Sterling Heights Assembly Plant will be the company's first U.S. factory to build a fully electric vehicle alongside existing internal combustion engine (ICE) models. The company retooled conveyor systems and rearranged workstations to accommodate multiple pickup truck models on the same line.
Honda is retooling its Marysville, Ohio, plant to produce ICE vehicles and EVs on the same assembly line. They are reimagining their approach to manufacturing with line consolidation and improved parts delivery.
Volkswagen Group’s Porsche Division retooled its Leipzig factory to produce gas, hybrid, and electric models on a single assembly line. A major overhaul was required for the "marriage" process between the chassis and body, necessitating the expansion of assembly stations, incorporation of additional robots, and development of an automatic screw-loading system.
Trumpf + Intrinsic [Trumpf]
TRUMPF, a leading company in machine tools and sheet metal fabrication, has partnered with Intrinsic to integrate AI innovation into machine tools, aiming to unlock new levels of productivity for users affordably and seamlessly. Together, they have developed AI-enabled solutions such as the TRUMPF SortMaster Vision, which automates the end-to-end cutting and sorting of sheet metal parts. Built using Intrinsic's Flowstate developer environment, SortMaster Vision allows robots to autonomously sort metal pieces using cameras and deep learning algorithms trained solely on CAD files. This eliminates the need for manual programming or robotics expertise, enabling customers to adapt to new parts and batch sizes quickly.
How AI Enables New Possibilities in Chemicals [McKinsey]
A McKinsey Global Institute survey highlights that only 14% of energy and materials companies, including those in the chemical sector, currently leverage generative AI tools, compared to a cross-industry average of 23%. Despite this lag, generative AI offers transformative opportunities for the chemical industry, which depends on scientific data for innovation, grapples with fragmented customer information, and navigates complex manufacturing processes. Generative AI can synthesize insights, create new content, and reveal patterns in critical areas like customer acquisition, molecule discovery, and new material applications by processing structured and unstructured data- such as lab notes, technical specifications, and CRM records. In R&D, generative AI can accelerate the discovery of molecules and materials by two to three times, uncovering patentable chemistries optimized for specific end-product properties. It can also shorten formulation timelines by over 30% and reduce costs by approximately 5%. For instance, Google DeepMind has predicted the structures of 2.2 million new materials, with over 700 synthesized and undergoing lab testing. Beyond R&D, generative AI enhances maintenance labor productivity by 30–40% through predictive maintenance, improves yield and throughput by over 10%, and reduces customer service-related lost sales by more than 65% while cutting administrative costs by over 50%. AI-driven models also process vast manufacturing data to refine maintenance strategies, optimize production schedules, and streamline supply chains. As adoption grows, generative AI has the potential to redefine efficiency and innovation in the chemical industry, driving both scientific breakthroughs and operational excellence.
To Challenge China, India Must Get Out of the Way of Its Factory Owners [WSJ]
India aspires to transform its manufacturing sector into an economic powerhouse but faces significant internal challenges, particularly in labor-intensive industries like garment manufacturing. Despite opportunities from global shifts—such as Donald Trump’s promise of high import tariffs on Chinese goods, which could favor Indian exports—manufacturers encounter persistent obstacles. Factory owners like A. Dhananjaya in Bangalore struggle with high labor costs and complex compliance regulations. To avoid burdensome requirements like additional licenses and expenses, Dhananjaya keeps his workforce below 100 employees. This strategy has limited his ability to scale, forcing him to lay off half his workers in recent years as he loses business to more efficient factories in China and Bangladesh. Regulatory hurdles further deter expansion. Factories with over 100 employees need government approval to terminate workers, and those employing at least 50 women must provide on-site nurseries. Introducing a second shift requires prior approval, restricting operational flexibility. Attempts by the government to ease labor laws—such as allowing firms with up to 300 employees to fire workers without approval—have faced strong resistance from labor unions. Additionally, India'’s lack of free-trade agreements diminishes its global competitiveness. Indian garments face higher tariffs in international markets, while steep duties on synthetic fabrics used in fast-fashion production further disadvantage manufacturers. This challenging environment has even led domestic retailers to source from Bangladesh, driving a rise in India'’s apparel imports. Without meaningful reforms to reduce regulatory barriers and improve trade competitiveness, India risks missing a crucial opportunity to establish itself as a global manufacturing leader.
Research:
2025 Manufacturing Industry Outlook [Deloitte]
In 2024, U.S. manufacturing experienced continued investment despite higher interest rates and a challenging business environment. In 2025, manufacturers anticipate a complex and uncertain business climate due to higher costs, potential policy changes following U.S. and global elections, and geopolitical uncertainty. Manufacturers surveyed in NAM's Q3 2024 outlook expect raw material and input costs to grow by 2.7% over the next 12 months. While lower interest rates could spur investment and consumer spending, potentially increasing demand for manufactured goods, there is a risk that unemployment could accelerate, leading to an economic slowdown.
Key Trends for 2025:
Talent Management:
Labor Market Dynamics: In July 2024, the number of unemployed in manufacturing exceeded job openings for the first time since May 2021.
Turnover Costs: A 2024 survey of over 300 HR leaders at U.S. manufacturing companies found that 60% reported the average cost to replace one skilled frontline worker ranges from $10,000 to $40,000. Additionally, 56% said employee turnover has a moderate to severe impact on bottom-line finances.
Future Workforce Shortage: The labor market in manufacturing has stabilized, with employment leveling off at around 13 million workers. The quits rate dropped to 1.6% in September 2024, a 0.2 percentage point decrease since January 2024. However, talent challenges persist; nearly 60% of manufacturers in the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM) third-quarter 2024 outlook survey cited the inability to attract and retain employees as their top challenge.
Strategies: Companies are improving worker experience, adopting advanced talent planning and workforce management tools, and focusing on upskilling to reduce turnover and prepare for demand volatility. Over 80% of large businesses with hourly employees are expected to invest in advanced workforce management software by 2025.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Generative AI:
Adoption Rates: 55% of surveyed industrial product manufacturers already leverage generative AI tools, and over 40% plan to increase investment in AI and machine learning over the next three years.
Strategic Implementation: 78% of manufacturers indicate their AI initiatives are part of the company’s overall digital transformation strategy.
Data Challenges: Nearly 70% report that data quality, contextualization, and validation are significant obstacles to AI implementation.
Customer Experience Focus: 74% of manufacturers plan to use or already use generative AI to enhance customer experience.
Investment in Data Management: Three-quarters of respondents have increased investment in data life cycle management to support their generative AI strategy.
Supply Chain Management:
Persistent Disruptions: Supply chains have improved but haven’t returned to pre-pandemic norms. The average delivery time for raw materials dropped to 81 days by October 2024, representing a 2% year-over-year decline.
Labor Shortages: Over 80% of manufacturing professionals indicated that labor turnover disrupted production in 2024. The truck driver shortage continues and is expected to worsen.
Cost Increases: Over 35% of surveyed manufacturers cited transportation and logistics costs as a primary business challenge in the third quarter of 2024.
Investment in Technology: 78% of manufacturers have implemented or plan to invest in supply chain planning software. Digital tools are leveraged for advanced planning, simulation, and enhanced visibility.
Smart Operations:
Digital Transformation Progress: 98% of surveyed manufacturers have started their digital transformation journey, up from 78% in 2019.
Increased Technology Investment: Technology investments accounted for 30% of operating budgets 2024, compared to 23% in 2023.
Top Technologies: Cloud computing, generative AI, and 5G offer the greatest return on investment. 34% of industrial product manufacturers plan to invest in 5G technology over the next one to three years.
Extended Reality (XR) and AI: Nearly 30% plan to invest in XR technologies, and more than 40% plan to invest in AI and machine learning.
Simulation Use Cases: Process simulation is the top use case for metaverse technologies; higher throughput and reduced costs are the primary benefits realized.
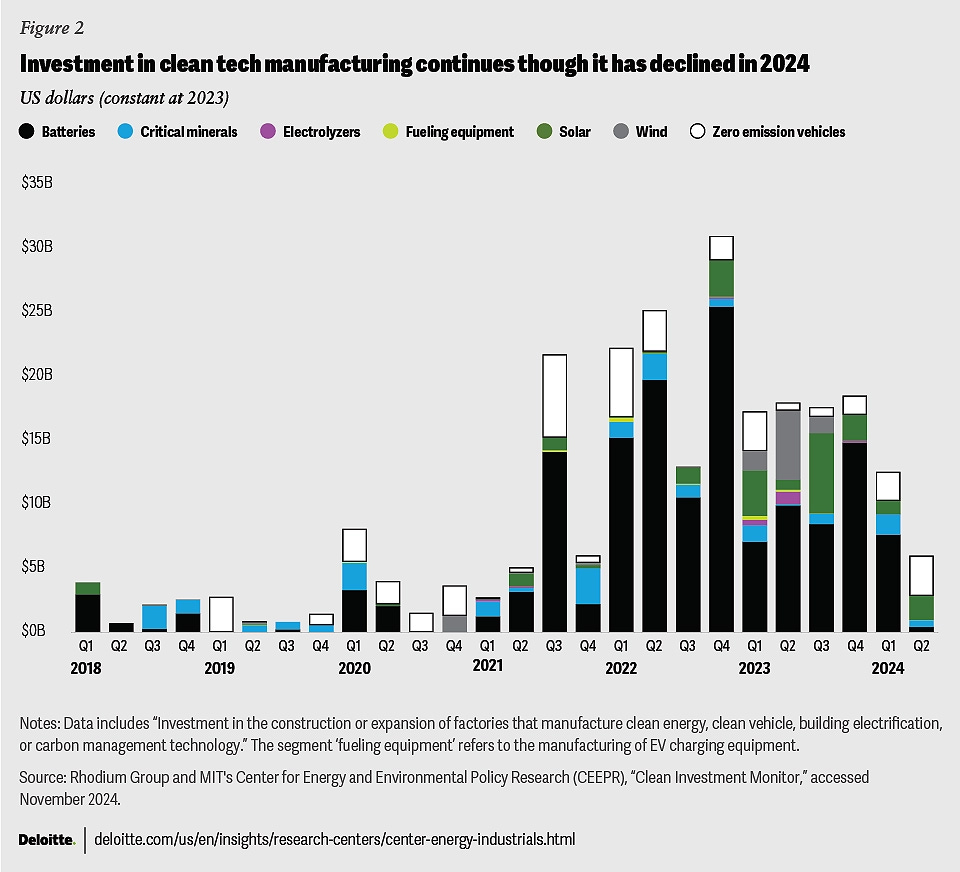
Clean Technology Manufacturing:
Investment Trends: Investment in clean technology manufacturing totaled over $31 billion across 192 facilities in 2024 through October, expected to create close to 27,000 new jobs.
Automotive Sector Adjustments: Some automakers have reduced investment in electric vehicles due to slower adoption rates.
Commitment to Decarbonization: Industrial manufacturers continue to invest in electrification and decarbonization. Reports mentioning”"electrificatio”" or”"scope three emission”" have increased since 2020.
Strategic Investments: Companies are making cautious, targeted investments to meet net-zero targets, considering potential policy shifts, interest rates, and cost pressures.
Podcasts/Video:
The New Cobot Proxie
Manufacturing Deals🏭💵
Roboflow - A company building a platform to build and deploy computer vision applications
40 million [Series B] - Led by GV by joined by Craft Ventures and YC
BrightAI - A company building an AIoT copilot platform for modern infrastructure
$15 million [Seed] - Led by Upfront Ventures
Juna.ai - A german company building an Agentic Process Control platform to help maximize production throughput and increase energy efficiency
$7.5 million [Seed] - From Kleiner Perkins, Norrsken VC, and John Doerr.
Ubitium - A company developing the universal RISC-V microprocessor
$3.7 million [Seed] - From Runa Capital, Inflection, and KBC Focus Fund
Downtime 🏭🧑🔧
Becoming Bob Dylan