Breaking the Bottleneck | Issue 74
[3/11/2024] Backflip AI, Humanoids, ABB's Manufacturing Outlook, & More!
Breaking the Bottleneck is a weekly manufacturing technology newsletter with perspectives, interviews, news, funding announcements, manufacturing market maps, and a startup database!
💥 If you are building, operating, or investing in manufacturing, hardware, or robots, please reach out. My email is aditya@schematicventures.com – I’d love to chat!
🏭 If you were forwarded this and found it interesting, please sign up!
Content I Enjoyed Last Week 🗞️🔬 📚
News:
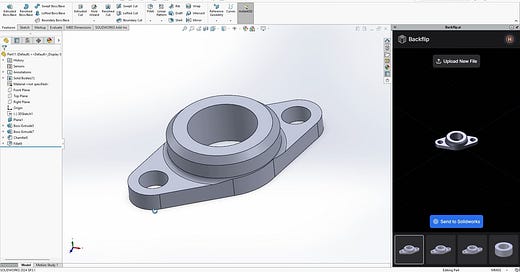
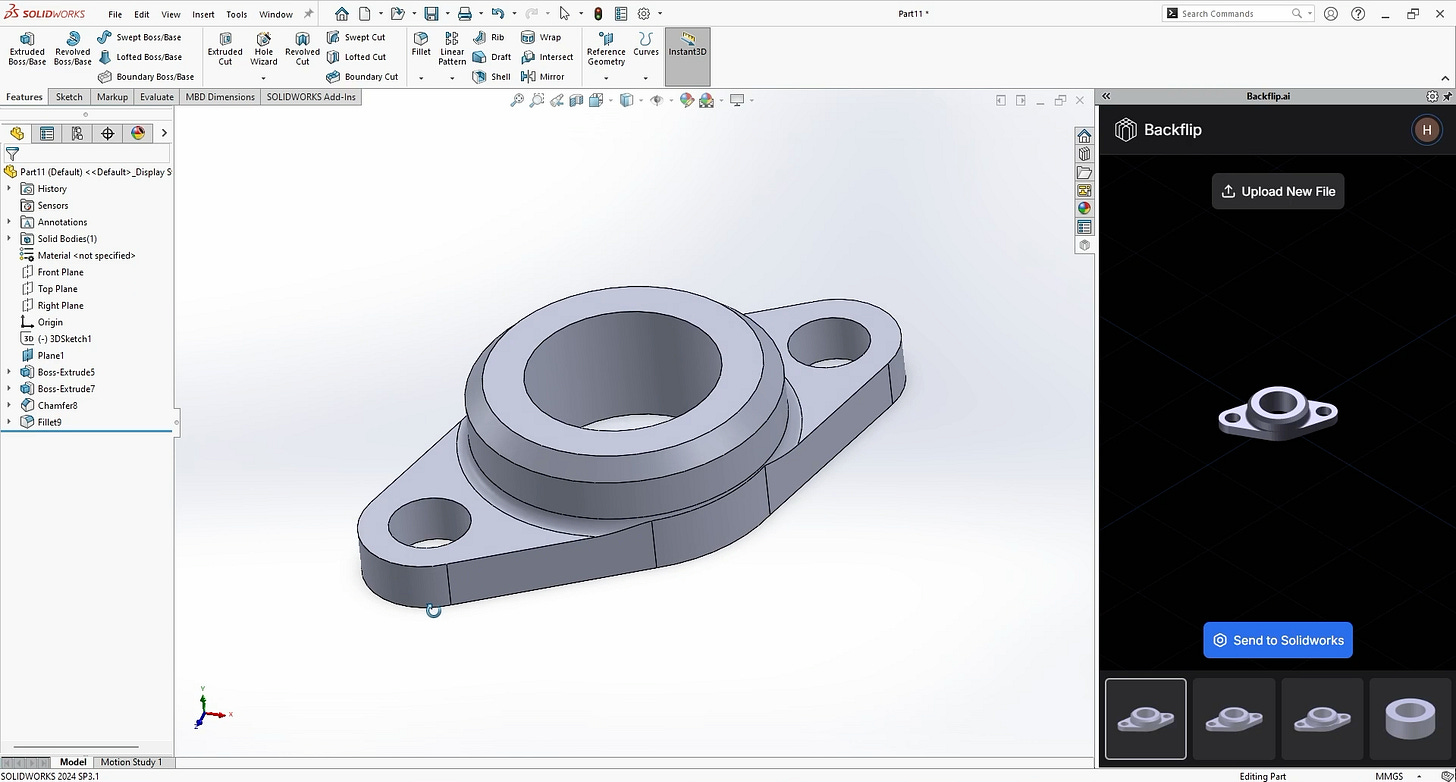
AI Can Now Use Solidworks [Engineering.com]
Backflip, a generative AI startup specializing in text-to-3D modeling, has introduced a groundbreaking AI tool that converts mesh data into parametric CAD models, a significant advancement in reverse engineering and digital design workflows. Unlike traditional mesh files, which represent only geometric data, parametric CAD models are precise, editable, and manufacturable, making them indispensable for engineering applications. Backflip’s AI automates this traditionally time-consuming and expertise-dependent process by analyzing a 3D scan mesh, predicting feature tree steps, and directly generating a SolidWorks-native model in 30 to 60 seconds. The tool, available as a web app and SolidWorks plug-in, provides users with four editable CAD model options, making it a potential game-changer for manufacturers who need to repair and replace parts without requiring CAD expertise. While the AI is currently optimized for simple mechanical components, Backflip plans to enhance its capabilities and allow companies to fine-tune models based on their own CAD data. At 3DExperience World 2025, Dassault Systèmes announced its own mesh-to-parametric CAD feature for SolidWorks, though its release timeline remains unclear. Additionally, Dassault’s 3DLive app for the Apple Vision Pro will enable virtual interaction with 3DExperience platform data, supporting engineering collaboration and product visualization. Meanwhile, Creaform introduced Scan-to-CAD Pro, an upgraded reverse engineering module within its Metrology Suite, offering 2D sketching and 3D modeling features to enhance the transition from 3D scanning to CAD design.
Amazon Debuts’s First Quantum Computing Chip [MIT Tech Review]
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has unveiled Ocelot, its first-generation quantum computing chip, marking a significant step toward scalable and hardware-efficient quantum systems. Ocelot features nine qubits, including five “cat qubits”, microwave-containing tantalum structures, and four transmon qubits, which monitor and correct errors in the cat qubits. Unlike quantum processors from Google and IBM, which rely solely on transmons, AWS’s hybrid cat-transmon design significantly reduces the hardware overhead for error correction, addressing a fundamental challenge in quantum computing. Google’s quantum computer required 105 qubits to encode a single error-corrected bit, whereas AWS’s approach achieves the same correction with just nine qubits, a 90% reduction in qubit overhead. This streamlined design makes it theoretically easier to scale up quantum computing hardware while maintaining high error correction efficiency. While Ocelot currently serves as a quantum memory demonstration, AWS plans to expand the number of qubits, improve computational capabilities, and solve scaling challenges such as inter-chip connectivity and wiring complexities. Despite the milestone, quantum computing remains far from commercial viability, with experts estimating that thousands to millions of qubits will be required for practical applications. Nonetheless, AWS’s Ocelot marks a critical advance in reducing quantum hardware complexity, making scalable, fault-tolerant quantum computers more feasible in the long term.
EVs Made These Engineers Expendable [IEEE Spectrum]
Ford engineer Lem Yeung, a 30-year veteran in internal-combustion-engine (ICE) development, faced a career-defining moment in 2021 when he received an early retirement buyout amid Ford’s shift toward electric vehicles (EVs). Despite his deep expertise, having worked on everything from the 6.7-liter Power Stroke “Scorpion” diesel engine to smaller four-cylinder engines, Yeung saw his role diminish as Ford redirected investments into EVs. Under CEO Jim Farley, Ford aggressively restructured its workforce, replacing ICE engineers with EV specialists from Silicon Valley and prioritizing battery and software-driven talent. This shift mirrored an industry-wide transformation, where EV powertrains, with far fewer moving parts, required less intricate engineering than traditional engines. While Yeung admired EVs’ instant torque and efficiency, he lamented that they lacked the artistry and complexity that defined ICE development. Once a defining skill of the auto industry, power-train engineering was rapidly becoming obsolete, with new engine programs dwindling from nearly 70 in 2011 to just five in 2021.
Ford’s EV transition is part of a larger upheaval in the global auto industry, where traditional automakers face increasing competition from Tesla, BYD, and battery giants like LG and Panasonic. Despite decades of dominance in mechanical engineering, legacy car companies now struggle to differentiate themselves in an era where EV components are essentially modular and commoditized. Yeung and his peers believe that Detroit’s historical competitive advantage, mastery over complex ICE powertrains, is eroding, leaving companies like Ford vulnerable in a market where software expertise and battery cost-efficiency matter more than mechanical innovation. With fewer barriers to entry, Chinese EV firms and tech-driven automakers are outpacing Western incumbents, leveraging lower-cost battery setups and advanced software integrations. Yeung ultimately viewed Ford’s pivot as a potential strategic misstep, where the company risks losing its identity and engineering edge in a new EV landscape that favors tech-first innovators over century-old manufacturers.
Humanoid Robots Finally Get Real Jobs [WSJ]
Humanoid robots are increasingly being integrated into the warehouse and industrial settings, as seen with Agility Robotics’ Digit, which now operates in a Spanx distribution center run by GXO Logistics. These robots are a flexible bridge between traditional automation systems, performing tasks like carrying bins and loading conveyor belts. The shift toward humanoid robots is driven by falling hardware costs, advancements in AI, and the need for adaptable automation that can handle multiple tasks within dynamic environments. Unlike traditional robots designed for single functions, humanoid robots benefit from human-like dexterity, spatial awareness, and the ability to navigate environments designed for people, such as stairs and shelves. While still expensive, their increasing versatility and adaptability make them a promising long-term investment, with companies like Apptronik, Boston Dynamics, and Unitree developing cost-effective, scalable solutions. Advances in simulation-based training, such as those pioneered by Boston Dynamics and Nvidia, are making robots more autonomous and capable than ever. However, current humanoid robots remain limited in functionality, and high-cost deployments remain rare. For example, inside the Spanx warehouse, only two Digit robots are operational. Industry experts, including Ohio State’s Ayanna Howard, believe that while humanoid forms will have a place, the future of general-purpose robotics may involve modular designs that allow for robotic torsos to be placed on various mobility platforms rather than strictly mimicking human bodies.
Boston Dynamics’ Atlas Humanoid Learns to Sequence Auto Parts [Robot Report]
The Missing Productivity Ingredient: Investment in Frontline Talent [McKinsey]
Finding skilled workers is increasingly difficult due to demographic shifts, widening skill gaps, generational disconnects, and stagnant wages, making productivity gains elusive. Despite heavy investments in automation, AI, and robotics, many companies struggle to realize expected gains, with McKinsey estimating that only one-third of digital transformation benefits are typically captured. Labor productivity leaders, however, take a different approach by viewing frontline workers as assets rather than costs to minimize. On average, businesses spend three times more on talent than capital assets, yet few rigorously assess the return on investment (ROI) in labor, leading to missed opportunities. Companies that optimize workforce planning and compensation, reimagine work environments, and integrate automation effectively achieve higher total shareholder returns (TSR) and labor productivity growth. For U.S. manufacturers, the cost of labor instability-high attrition, absenteeism, and vacancies can reach $17,000 to $30,000 per employee, translating to a $250 million EBITDA impact for a 10,000-person workforce.
Top-performing companies stand out by excelling in seven key workforce strategies. First, they reassess compensation beyond short-term incentives, with companies like Unilever ensuring living wages and Ingersoll Rand awarding $250 million in stock grants to boost employee retention. Second, they redesign workflows using automation to improve safety and efficiency, as seen in Waste Management’s robotic trucks and Chipotle’s avocado-peeling machine. Third, they optimize workforce planning, with companies like Land O’Lakes implementing flexible shifts to improve retention. Fourth, they invest in talent attraction, as Quanta Services has spent $150 million on workforce development, doubling revenue growth relative to headcount expansion. Fifth, they measure talent effectiveness, with Unilever’s incentives reducing absenteeism by 50% and increasing productivity by 10%. Sixth, they cultivate strong workplace cultures, as one manufacturer’s employee suggestion platform generated $1 million in annual cost savings. Finally, they emphasize training and development, with companies either partnering with universities or developing in-house programs to meet cutting-edge industry needs.
Infrastructure Announcements:
Lilly to Spend $27 Billion to Bolster US Drug Manufacturing [Bloomberg]
Apple Will Add 20,000 US Jobs [Bloomberg]
Research:
ABB & AMS Automotive Manufacturing Outlook Survey [ABB]
ABB Robotics’ 2025 Automotive Manufacturing Outlook Survey reveals that 82% of manufacturers see AI as crucial for cost reduction in auto production, with 64% expecting increased adoption of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs)to enhance efficiency. The study underscores the industry’s shift toward smart factories, leveraging AI-powered robotics, digital twins, and flexible manufacturing to streamline production, reduce energy consumption, and accelerate model introductions. 73% of respondents predict greater adoption of digital twinning and simulation technologies, while 57% anticipate more collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside humans to automate repetitive tasks. The survey also highlights the growing importance of flexible manufacturing, with 84% of manufacturers identifying it as key to adapting to fluctuating demand across EVs, hybrids, and internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles without major capital investment. Despite the positive outlook, several challenges remain: 54% cite high initial costs, 35% mention technical hurdles, and 32% express concerns over cybersecurity, data protection, and workforce adaptation.
Teaching Robots to Listen and Think Harder [Physical Intelligence]
Hi Robot is a novel hierarchical interactive robotic system that integrates vision-language-action (VLA) models, such as π0, with a two-level inference process to enhance robotic decision-making and adaptability. Inspired by Daniel Kahneman’s System 1 (instinctive, reactive behavior) and System 2 (deliberative, reasoning-based decision-making), Hi Robot enables robots to “talk to themselves” when executing complex tasks. π0 serves as the low-level, fast, and reactive policy that handles well-practiced tasks, while a high-level vision-language model (VLM) acts as the reasoning system, breaking complex tasks into manageable subtasks and dynamically responding to real-time corrections. The high-level policy processes open-ended instructions and visual inputs from base and wrist-mounted cameras, generating step-by-step commands for π0. This allows the system to incorporate user feedback, such as recognizing an object that should not be discarded while cleaning. By leveraging pre-trained VLMs, Hi Robot improves reasoning by utilizing web-scale knowledge, similar to how humans reference prior learning when solving new problems. Unlike a standard flat VLA model, Hi Robot structures tasks hierarchically, improving accuracy and adaptability.
Experimental results demonstrate that Hi Robot outperforms both GPT-4o and flat VLA models across real-world tasks such as table bussing, sandwich making, and grocery shopping. It achieves 40% higher instruction-following accuracy than GPT-4o and substantially better task progress scores by correctly interpreting multi-step instructions and modifying behaviors based on real-time user input. The broader goal of Hi Robot is to build robots capable of common-sense reasoning in open-world settings. By integrating large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs) with physical control, the system aims to enable robots to understand context, handle fragile objects delicately, recognize when not to disturb a sleeping person, and infer meaning from environmental cues (e.g., “do not erase” written on a whiteboard).
Manufacturers’ Outlook Survey: First Quarter 2025 [NAM]
The National Association of Manufacturers Q1 2025 Manufacturers’ Outlook Survey reveals growing concerns over trade uncertainties and increased raw material costs. Trade uncertainties surged to the top of manufacturers’ challenges, cited by 76% of respondents, jumping 20 percentage points from Q4 2024 and 40 percentage points from Q3 of last year. Increased raw material costs came in second, cited by 62% of respondents. If Congress fails to act now on extending the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, 69% of survey respondents said they would delay purchasing capital equipment, while 45% would hold off on hiring, 45% would stall the expansion of operations, 41% would limit R&D investments and 40% would curb increases in employee wages or benefits. Other findings from the report:
Manufacturers expect prices on their company’s product line to increase by 3% over the next 12 months.
Manufacturers expect raw material prices and other input costs to rise 5% over the next year.
Manufacturers expect export sales to increase just 0.1% over the next 12 months, the lowest level since Q2 2020, the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
2025 Industrial Manufacturing Insights [KPMG]
Podcasts/Video:
When a Small Town Gets a Big Data Center [Big Take]
Finance & Transactions 💵
Venture Capital:
Zeitview - A company building the visual AI platform for critical infrastructure.
$60 million [Financing] - Led by Climate Investment and joined by Valor Equity Partners, Union Square Ventures, Upfront Ventures and more
Tandem PV - A company building a new solar design that boosts the output of conventional solar modules by combining them with thin-film perovskite.
$50 million [Equity & Debt] - Led by Eclipse Ventures and joined by Constellation Energy, Planetary, Uncorrelated Ventures, and Trellis Climate
Viam - A company building a web-connected, open source, plug and play platform for hardware development.
$30 million [Series C] - Led by USV and joined by Battery Ventures and Neurone
Capow - A company developing in-motion electric charging systems for robots
$15 million [Series A] - Led by Toyota Ventures
Glimpse - A company building the world’s most powerful battery quality monitoring program.
$10 million [Series A] - Led by TDK and joined by Ibex Mobility and Flybridge Capital Partners.
Planned Downtime 🧑🔧
Robert De Niro Talks Through His Characters [GQ]