Breaking the Bottleneck | Issue 75
[3/17/2024] Solid State Batteries, Green Steel, Fictiv's 2025 State of Manufacturing and Supply Chain, & More!
Breaking the Bottleneck is a weekly manufacturing technology newsletter with perspectives, interviews, news, funding announcements, manufacturing market maps, and a startup database!
💥 If you are building, operating, or investing in manufacturing, hardware, or robots, please reach out. My email is aditya@schematicventures.com – I’d love to chat!
🏭 If you were forwarded this and found it interesting, please sign up!
Content I Enjoyed Last Week 🗞️🔬 📚
News:
A Big Milestone for Green Steel Production [MIT Tech Review]
Boston Metal has successfully demonstrated its molten oxide electrolysis (MOE) technology at an industrial scale, producing over a ton of steel in its largest reactor to date. Unlike traditional blast furnaces that rely on coal-based coke, Boston Metal’s process uses electricity to extract iron from ore, emitting only oxygen instead of carbon dioxide. If powered by renewable or nuclear energy, this method could significantly reduce the 3 billion metric tons of CO₂ generated annually by steel production. The company has spent over a decade scaling its technology from lab-sized reactors to multi-ton production, refining key components like inert anodes, which enable the electrochemical reaction without degrading. The latest successful test proves the viability of multi-anode reactors, a crucial step in making the process scalable for commercial steel production. The next phase involves constructing a larger demonstration plant, set to begin operations in 2027, which will produce in a single day what the current system generates in a month. Boston Metal aims to license its technology to major steel manufacturers, providing a zero-emissions alternative to conventional steelmaking. This milestone aligns with broader industry efforts, such as Sweden’s Stegra, which raised $7 billion to develop green hydrogen-based steel.
Mercedes-Benz Drives Toward Solid-State EV Batteries [IEEE Spectrum]
Mercedes-Benz and Factorial Energy have reached a key milestone in solid-state battery development, road-testing semi-solid-state lithium-metal cells in the EQS electric sedan. These Factorial Electrolyte System Technology (FEST) cells deliver 391 Wh/kg energy density, significantly outperforming high-nickel lithium-ion batteries at 300 Wh/kg or less. The prototype battery allows for a 1,000 km (620-mile) range, about 25% longer than conventional batteries of the same size and weight. Factorial also develops fully solid-state “Solstice” cells with a sulfide electrolyte, targeting up to 500 Wh/kg for an 80% longer range. The quasi-solid-state design enables lithium-metal anodes that replace graphite, boosting energy storage and efficiency while maintaining compatibility with existing lithium-ion battery manufacturing. It allows battery makers to use 80% of their existing production equipment with minimal investment. Mercedes’ Formula 1 division engineered a patented floating cell carrier to manage the expansion and contraction of the pouch cells during charging cycles, improving efficiency and durability. Factorial is scaling production with an annual capacity of 500,000 FEST cells and 85% battery yield at its pilot facility, though commercial viability requires a 95% yield. The company, backed by $200 million in funding from Mercedes and Stellantis, is also supplying Dodge Charger Daytona demonstration fleets expected to launch in 2026. Factorial’s dry-cathode process eliminates hazardous solvents, making battery production more sustainable and cost-effective. The company joins other solid-state battery leaders, including QuantumScape (Volkswagen), Solid Power (BMW), and Toyota, which are collectively pushing toward 2030 commercialization. If successful, solid-state batteries could revolutionize EVs by enabling faster charging, longer range, and reduced costs, potentially cutting battery pack sizes in half while improving performance and efficiency.
Foxconn Unveils First Large Language Model 'FoxBrain' [Foxconn]
Foxconn, the world’s largest contract electronics manufacturer, has developed its own large language model (LLM), FoxBrain, with reasoning capabilities and trained it in just four weeks. Initially built for internal use, FoxBrain specializes in data analysis, mathematics, reasoning, and code generation. The company trained the model using 120 Nvidia H100 GPUs, leveraging support from Nvidia’s Taiwan-based supercomputer and technical consulting. FoxBrain is built on Meta’s Llama 3.1 architecture and is Taiwan’s first advanced LLM with reasoning capabilities optimized for traditional Chinese language processing. While Foxconn acknowledges that FoxBrain is slightly behind China’s DeepSeek AI models, it claims the model is approaching world-class performance levels. Foxconn plans to release more details at Nvidia’s annual technology conference in mid-March. As the company faces shifting industry trends and declining profitability in its core electronics manufacturing business, it is aggressively expanding into AI and electric vehicles (EVs) to diversify its operations. The development of FoxBrain signals Foxconn’s strategic push into AI-driven automation, positioning itself as a leader in AI-powered manufacturing and supply-chain intelligence.
Qualcomm Acquires Edge Impulse [Edge Impulse]
Qualcomm has agreed to acquire Edge Impulse, a company specializing in AI-powered edge computing solutions, to enhance its Dragonwing AI and IoT platform. Edge Impulse simplifies the process of deploying machine learning models on resource-constrained edge devices, covering industries such as healthcare, industrial IoT, security, energy, and supply chain management. The company provides an end-to-end AI development workflow, allowing developers to collect data, train models, optimize performance, and deploy AI models with minimal manual effort. Integrating with Qualcomm’s AI stack will extend Edge Impulse’s reach to 170,000 developers, enhancing support for computer vision, speech recognition, and generative AI on Qualcomm’s MCUs, CPUs, GPUs, and NPUs. Edge Impulse’s tools will integrate with Qualcomm’s AI Hub and Foundries.io, enhancing model testing, deployment, and optimization capabilities. Nakul Duggal, Qualcomm’s General Manager for automotive, industrial, and embedded IoT, highlighted the acquisition’s potential to expand AI capabilities across multiple industries, reinforcing Qualcomm’s commitment to AI, IoT, and real-world AI applications. The move aligns with Qualcomm’s broader AIoT (AI + IoT) vision, combining advanced AI inference, cloud connectivity, and developer tools to support next-generation AI applications in industrial and enterprise sectors.
How AI Agents Are Accelerating Digital Transformation [PTC]
AI-driven intelligent software agents are revolutionizing manufacturing by automating routine tasks, optimizing supply chains, and accelerating product development. By integrating AI into enterprise systems, manufacturers can increase productivity by 30%, reduce costs, and enhance decision-making. Generative AI and AI agents enable seamless interaction with industrial data through natural language processing, real-time analysis, and automated workflows. These AI-powered tools enhance engineering design, service operations, and supply chain logistics, allowing workers to focus on innovation rather than administrative processes. Leading manufacturers are embedding AI agents into PLM, ALM, FSM, and ERP systems, ensuring digital traceability, automated change management, and virtual product validation. Integrating AI agents into manufacturing ecosystems enables a progressive shift from manual to autonomous operations, optimizing design, production, and service workflows. The AI agent tech stack comprises four key layers: User Engagement, Application Services, Data Management, and Software Ecosystem. AI agents function at different levels: assistive, augmentative, or autonomous, gradually increasing efficiency and automation. Vector databases, semantic layers, and APIs allow AI to extract and apply insights across complex industrial environments. AI-powered traceability agents monitor design modifications, change management agents predict engineering dependencies and validation agents generate compliance test scenarios. While manufacturers face challenges in data management, workforce adaptation, and regulatory compliance, they benefit from AI advancements, cloud-based scalability, and digital transformation initiatives.
Research:
Google Brings AI To The Physical World [Deepmind]
Google DeepMind has introduced Gemini Robotics and Gemini Robotics-ER, two AI models based on Gemini 2.0, designed to enhance embodied reasoning for real-world robotic applications. Gemini Robotics, a vision-language-action (VLA) model, allows robots to generalize across new environments, respond to natural language commands, and perform fine motor tasks with greater dexterity. The model adapts to different robotic platforms, including bi-arm systems like ALOHA 2 and Franka and humanoid robots like Apptronik’s Apollo. Meanwhile, Gemini Robotics-ER enhances spatial reasoning and allows roboticists to integrate Gemini’s AI with existing low-level controllers. It significantly improves object detection, pointing, 3D spatial awareness, and dynamic task execution, with 2-3x better performance than Gemini 2.0. The system leverages in-context learning, enabling robots to grasp objects and plan movement trajectories intuitively. DeepMind emphasizes safety and responsible AI development, integrating Gemini Robotics-ER with collision avoidance and force-limiting systems while enabling semantic safety measures via a data-driven “Robot Constitution.” This framework allows users to create and modify rules that guide robotic actions in real-world settings. To advance research, DeepMind is releasing ASIMOV, a dataset for evaluating safety in robotics, and collaborating with industry leaders like Agility Robotics, Boston Dynamics, and Enchanted Tools. These models mark a significant step toward general-purpose robots capable of performing complex, multi-step tasks in homes, workplaces, and industrial settings.
2025 State of Manufacturing and Supply Chain [Fictiv]
Fictiv published its 10th Annual 2025 State of Manufacturing & Supply Chain Report, revealing what’s top of mind for manufacturing and supply chain leaders. Below are some of the key takeaways:
Growing Global Business Uncertainty
Trade war concerns are escalating, with 93% of leaders worried about potential tariff increases, up from 89% in 2024. 96% anticipate the U.S. administration’s policies will impact supply chains, affecting costs and profitability (57%).
Onshoring and nearshoring are gaining traction, with 53% prioritizing localized manufacturing to mitigate risks. India is emerging as a key sourcing region due to lower tariffs and firm export commitments.
Accelerating Supply Chain Disruptions
77% of leaders cite a lack of resources as a top challenge, including supplier quality, reliability, and budget constraints.
52% report supplier quality as a primary concern, while 38% cite limited supply chain visibility as a significant issue.
Onshoring to the U.S. is a key strategy (68%), followed by nearshoring (50%) and diversifying global manufacturing operations (39%) to counter logistics challenges and tariff impacts.
Scaling Production Remains a Major Barrier
91% of companies face obstacles in new product innovation, with 49% struggling to source low-volume builds and 39% citing slow feedback loops as roadblocks.
Engineers spend more time on procurement, with 76% spending over four hours per week, diverting their focus from product innovation.
Digital manufacturing is seen as a solution, with 90% of leaders stating it is essential for streamlining production, reducing risk, and enhancing efficiency.
Sustainability Becomes a Core Priority
95% of leaders say climate change and extreme weather impact their supply chain strategy, driving the need for more resilient supplier networks and onshoring strategies.
92% of companies have sustainability initiatives, with 54% adopting recognized standards (e.g., ISO 14001).
Sustainability is influencing onshoring, with 79% of leaders prioritizing U.S. manufacturing to reduce environmental impact and increase supply chain control.
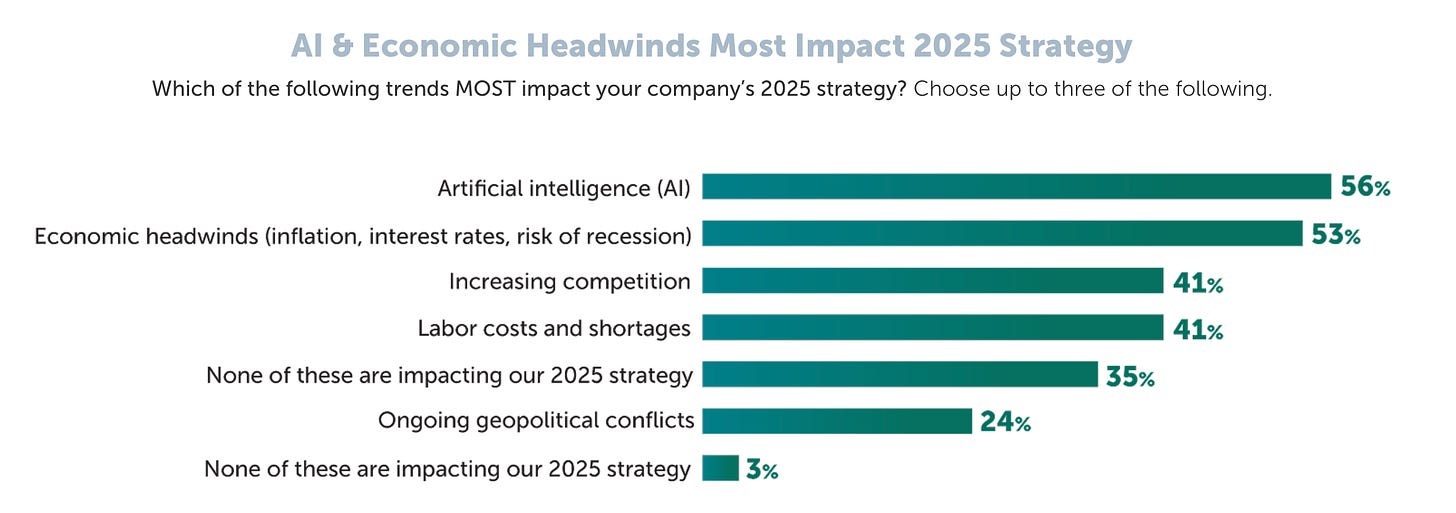
AI Advances in Supply Chain and Manufacturing
94% of companies use AI in supply chain operations, including inventory management, quality control, and machine operations.
87% report that their AI implementations have reached medium or high maturity, which signifies a shift from early experimentation to full-scale adoption.
Podcasts/Video:
Sci-Fi on the Factory Floor [BCG]
Finance & Transactions 💵
Venture Capital:
Lumafield - A company building advanced 3D X-ray and CT scanning technology for manufacturing.
$75 million [Series C] - Led by IVP and joined by G2 Venture Partners, Wellington Management, and insiders Spark Capital, DCVC, Kleiner Perkins, Lux Capital, and Matter Venture Partners.
Dexterity - A company building physical AI for logistics applications at enterprises.
$95 million [Financing] - Led by Lightspeed Venture Partners
Ditto - A company building the only mobile database with built-in edge device connectivity and resiliency.
$82 million [Series B] - Co-led by Top Tier Capital Partners and Acrew Capital
Scimplify - A company building a platform for the end-to-end development and manufacturing of specialty chemicals.
$40 million [Series B] - Co-led by Accel and Bertelsmann
Infinite Uptime - A company building predictive maintenance services & plant-reliability solutions.
$35 million [Series C] - Led by Avataar Ventures and joined by StepStone Group, LGVP, and insiders Tiger Global and GSR Ventures.
Augmenta - A company building an autonomous design platform for the built environment.
$10 million [Seed] - Led by Prelude Ventures and joined by Montage VC
Planned Downtime 🧑🔧
F1 — Official Trailer