Breaking the Bottleneck | Issue 83
[6/23/2024] Zoox's Factory, RCA Agents, Lifespan of Modern Appliances, 2025 State of Manufacturing & More!
Breaking the Bottleneck is a weekly manufacturing technology newsletter with perspectives, interviews, news, funding announcements, manufacturing market maps, 2025 predictions, and more!
💥 If you are building, operating, or investing in manufacturing, supply chain, or robots, please reach out - adityabreakingthebottleneck@gmail.com I’d love to chat!
🏭 If you were forwarded this and found it interesting, please sign up!
Interview & Startup Series 🎙️💬
Alongside the usual newsletter, I’m excited to launch a weekly interview series, “Friday 5,” starting in July. The series focused on navigating the industrial software landscape, featuring industrial operators, founders, tech providers, and more. If you are similarly enthusiastic and know people whom I should interview, I’d love to hear from you and connect!
Content I Enjoyed Last Week 🗞️🔬 📚
News:
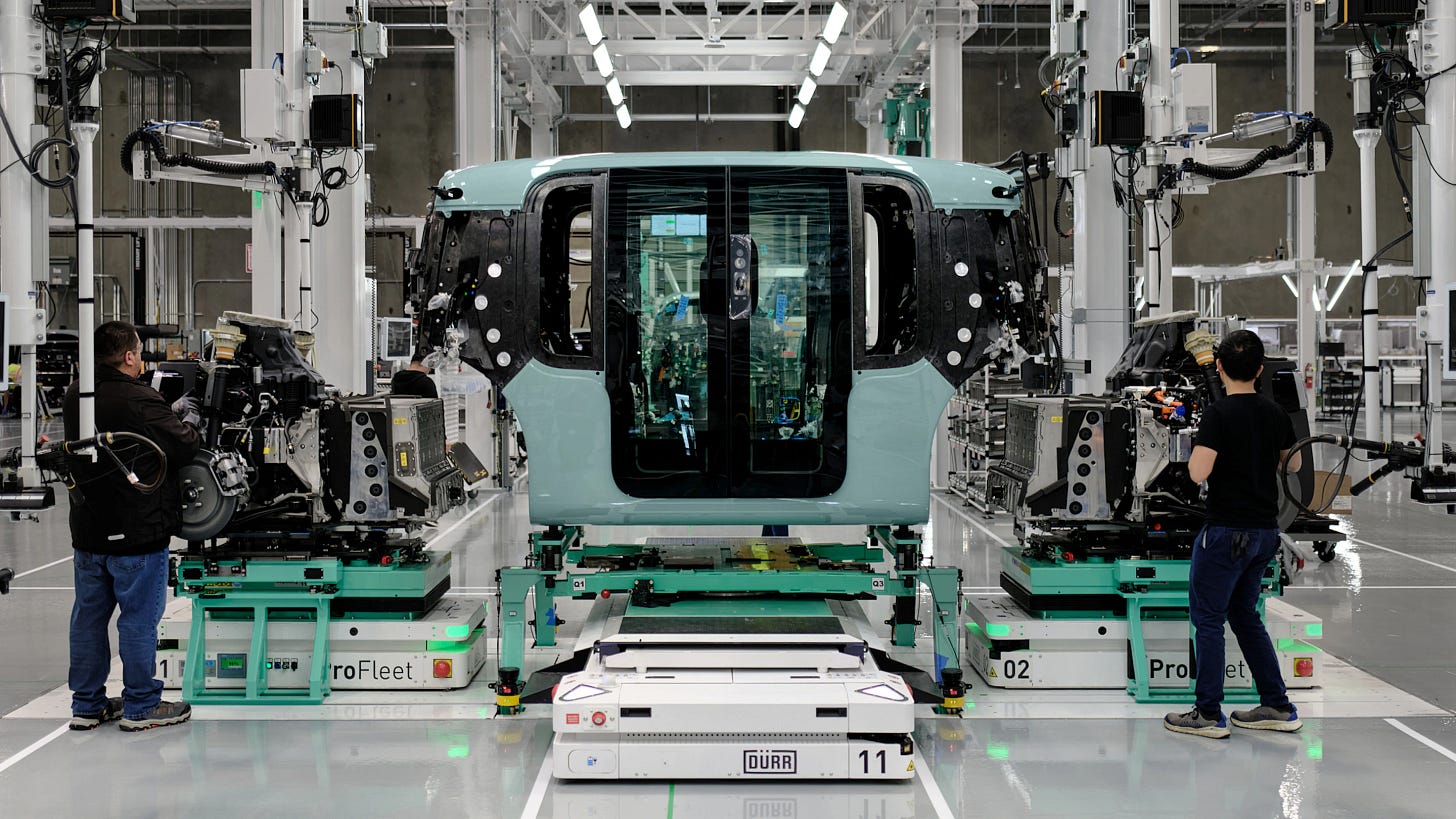
Inside the Zoox Robotaxi Serial Production Facility [Zoox]
Zoox has opened the first-ever serial production facility in the U.S. dedicated to assembling purpose-built autonomous robotaxis, marking a significant milestone in its commercialization journey. Located in Hayward, California, the 220,000-square-foot facility can produce over 10,000 robotaxis annually at full capacity and supports Zoox's service rollout starting in Las Vegas, followed by San Francisco, with future expansion to Austin and Miami. The site is used for robotaxi assembly, engineering integration, component storage, and end-of-line (EOL) testing. Unlike traditional carmakers, Zoox's facility avoids energy-intensive processes such as welding and painting, which contributes to its lower environmental footprint. The facility combines advanced robotics and human craftsmanship, utilizing automation for tasks such as glass installation while relying heavily on manual labor for precision assembly, thereby creating hundreds of jobs in the Bay Area. The modular, symmetrical design of Zoox’s robotaxi facilitates efficient and flexible assembly. Each vehicle undergoes rigorous End-of-Life (EOL) testing, which includes sensor calibration, alignment, dynamometer stress testing, rain simulation, and final inspections in a light tunnel and on a test track.
Other News:
Siemens & Altair Are On A Mission to “Transform Engineering” [Engineering.com]
Following Siemens’s $10 billion acquisition of Altair, executives from both companies, Sam Mahalingam (CTO, Altair) and Jean-Claude Ercolanelli (SVP of Simulation, Siemens Digital Industries Software), emphasized a strong cultural alignment and shared vision for innovation. Despite concerns about integration challenges, both leaders praised the seamless merger of engineering-focused values and technological excellence. Altair users can expect a complete rebranding under Siemens, with the eventual integration of Altair products into Siemens' Simcenter portfolio. Meanwhile, high-performance computing and AI tools may be housed under a separate yet-to-be-named umbrella. The overarching plan is to integrate the best elements of both platforms into a unified, future-facing simulation and design environment. A central focal point of the merger is artificial intelligence. Altair’s PhysicsAI, a deep-learning model trained on physics-based attributes such as geometry, materials, and load conditions, has been rapidly adopted—115 customer use cases were documented in a 2023 survey. Siemens and Altair are further developing AI-driven tools, including solver acceleration, AI documentation support, and virtual agent engineers capable of executing entire simulation workflows. In the long term, the duo aims to deliver intelligent lifecycle solutions via Siemens Xcelerator-as-a-Service, along with comprehensive digital twins and threads that span the entire product, manufacturing, and business lifecycles.
Why Do Appliances Have a Shorter Lifespan? [NY Times]
“[Modern appliances] are not made to last, they’re made to throw away.”
The decline in appliance durability is a multifaceted issue shaped by evolving consumer expectations, government regulations, globalization, and advancing technology. Although many Americans perceive a sharp drop in the lifespan of refrigerators, dishwashers, washers, and dryers, complex data reveals only modest declines since 2010. For example, the average lifespan of a front-load washer dropped from 11.1 years in 2010 to 9.1 years in 2019. Regulatory mandates for improved energy and water efficiency have prompted manufacturers to integrate complex electronics, such as sensors and circuit boards, into previously simple machines. While these changes promote sustainability and performance, they reduce repairability and increase the likelihood of component failure. Moreover, frequent model updates mean service technicians often struggle to keep up with evolving repair techniques and diagnostic tools, adding to consumer frustration. However, appliance longevity is not solely dictated by engineering or regulation; consumer behavior plays a significant role. Many buyers seek trendy features or sleek aesthetics, leading to replacements driven by "psychological obsolescence" rather than mechanical failure. The rise of feature-laden models adds complexity and potential points of failure. Simultaneously, price competition, particularly from global brands like Samsung and LG, has driven down costs at the expense of component quality, often favoring modular, non-repairable parts. Durability today is most reliably found either in stripped-down, analog models with few features or in high-end appliances with robust materials and long-term service plans. The average buyer, however, may need to adjust expectations, treating modern appliances more like smartphones or cars that trade longevity for convenience, complexity, and style.
Apollo is Leveraging Agentic AI-Powered Manufacturing Reasoner to Unlock Machine Insights [AWS Industries]
“The generative AI assistant reduces the DCT RCA from up to 7 hours per issue to less than 10 minutes per issue... saving approximately 15 million INR per year just in the passenger car radial (PCR) division.”
Apollo Tyres, a global tire manufacturer based in India, has significantly advanced its digital transformation by leveraging generative AI via Amazon Bedrock to enhance manufacturing efficiency. In collaboration with AWS, the company built a centralized data lake. It developed the “Manufacturing Reasoner”, a custom AI solution that automates root cause analysis (RCA) of curing press bottlenecks in real time. Previously, diagnosing issues in dry cycle time (DCT) across 250+ automated presses and 140+ SKUs required up to 7 hours per instance and necessitated the involvement of multiple subject matter experts. The new AI agent system now completes these tasks in under 10 minutes, offering sub-element-level diagnostics and dynamic visualization, resulting in an 88% reduction in manual RCA effort and projected annual savings of ₹15 million in the PCR division alone. The system also features real-time anomaly detection aligned with Poka-yoke error prevention principles. The solution integrates multiple Amazon Bedrock agents, including RCA, explainer, and visualization agents, utilizing natural language inputs through a user interface (UI) hosted on Amazon EC2. These agents interact with streaming IIoT data, AWS services such as Redshift and OpenSearch, and utilize Anthropic's Claude models for logic and visualization. The architecture was optimized to reduce latency from over a minute to around 30–40 seconds, and Apollo overcame early issues with visualization code generation for large datasets through iterative refinement. Plans involve scaling the generative AI framework to other manufacturing areas as Apollo progresses toward Industry 5.0. The project demonstrates how AI-enhanced tools can empower engineers to communicate with machines using natural language, automate diagnostics, and build intelligent, responsive factories.
A New Trade Paradigm: How Shifts in Trade Corridors Could Affect Business [McKinsey]
The global trade system is undergoing a profound transformation driven by rising geopolitical tensions, shifts in industrial policy, and the introduction of new tariff structures. McKinsey's analysis outlines three possible scenarios for trade through 2035: a baseline scenario where global trade grows by $12 trillion to $45 trillion; a diversification scenario, where supply chains are restructured for resilience, costing $1 trillion in trade growth; and a fragmentation scenario, where geopolitical distance reduces trade by up to $3 trillion. Trade flows could shift dramatically, with over 30% of trade potentially moving between corridors depending on the scenario. The biggest disruptions are likely in electronics, textiles, and machinery, where supply chains span geopolitically distant economies. Conversely, trade corridors between emerging economies (like China–ASEAN or India–Middle East) could prove resilient and even grow in adverse scenarios. Manufacturing value chains are especially vulnerable due to high geographic and geopolitical exposure. In electronics, for example, 58% of future trade value is at risk, with China alone responsible for 75% of global laptop exports. Trade corridors fall into three categories: safe bets (e.g., India–EU or China–ASEAN) that grow in all scenarios; cautious bets (e.g., Europe–Africa or advanced Asia–ASEAN) that grow slower under fragmentation; and uncertain bets (e.g., US–China or EU–Russia) which shrink in at least one scenario. Sectoral impacts vary; electronics and machinery face steep tariffs and structural exposure, while pharma and transport equipment remain relatively stable due to geopolitical alignment. In resource-rich sectors, globally concentrated industries like mining face lengthy diversification timelines and risk severe disruption, while energy and agriculture suffer from local concentration and infrastructure inertia. Companies are advised to rethink value creation and corridor prioritization strategies, building resilience through proactive investments, as Micron did by establishing a semiconductor facility in India.
Navigating the Dual Use Dilemma in Robotics [IEEE Spectrum]
Open-source robotics technologies, while crucial for innovation, collaboration, and democratized access, pose significant dual-use risks, as they can be repurposed for military or malicious use with minimal resources or expertise. Platforms like GitHub, ROS, and arXiv have accelerated global progress in robotics; yet, the same tools empower bad actors, ranging from rogue states to lone attackers, to develop autonomous or enhanced weaponized systems. Civilian drones adapted for warfare in Ukraine highlight this tension: while their use may be seen as a resourceful defense, the underlying accessibility also exposes global vulnerabilities. Robotics lacks the regulatory frameworks found in fields such as biology or nuclear engineering, leaving most researchers unequipped to evaluate the dual-use risks associated with their innovations. To address these challenges without stifling progress, the authors propose a four-part roadmap: education, incentives, moderation, and red lines. Education initiatives would embed responsible research practices and dual-use awareness into robotics curricula. At the same time, funding agencies and professional bodies, such as IEEE RAS, could incentivize risk assessments, establish ethical review boards, and promote peer-reviewed mitigation strategies. Community-driven moderation practices include gating high-risk open-source material, screening pre-publication content, and establishing tiered access to sensitive repositories. Finally, defining enforceable "red lines", such as banning the weaponization of general-purpose robots, could help anchor industry-wide ethics policies, including usage-based open-source licenses that revoke access for misuse. Companies like Boston Dynamics already advocate for such measures. The authors urge the robotics community to take proactive, self-regulatory steps to balance innovation with global security, warning that failure to do so could invite restrictive international regulations or societal backlash.
Product Announcements:
Generalist AI Launches Preview of Model Capabilities
Other Announcements:
Hexagon’s New Humanoid, Aeon, uses NVIDIA stack for developing and deploying physical AI systems and training foundation models.,
Duro’s announces new AI platform connecting design, supply chain, and manufacturing data through a unified digital thread.
PTC Launches Creo 12, and Onshape will soon be capable of Model-Based Definition (MBD).
Reshape Automation introduces the first end-to-end sales-acceleration platform explicitly designed for automation OEMs, system integrators, and distributors.
Blog / Research:
1XM World Model [1X]
1X has introduced the 1X World Model (1XWM) as a scalable simulation framework to evaluate generalist humanoid robot behavior, particularly its NEO model, in complex home environments. Instead of relying on slow, physical testing or rigid physics-based simulators, 1XWM predicts diverse futures for a robot based on sequences of actions, enabling faster iteration and architectural refinement. Trained on real-world robot observations, video frames, and action trajectories, 1XWM generates latent representations of future frames. It predicts task success, enabling the evaluation of policy performance across various scenarios, such as grasping a mug or wiping a counter. Unlike text-to-video models, 1XWM is action-controllable, simulating robot-specific behavior with physical accuracy. As training data scales, 1XWM's predictive fidelity improves. For example, interaction with an air fryer demonstrated enhanced understanding after exposure to task-specific data, moving from unrealistic predictions to precise modeling of object mechanics. Importantly, 1XWM allows 1X to forecast success rates across robot checkpoints and make high-confidence decisions without requiring real-world trials. By simulating counterfactuals for challenging scenarios, the model serves as an evaluation engine for benchmarking autonomous policies. It has shown a high correlation between simulated and real-world performance. With just 70% prediction accuracy, the model can identify the better-performing policy 90% of the time, even across significant gaps in success rates.
2025 State of Smart Manufacturing Report [Rockwell]
A few weeks back, Rockwell released the 10th edition of their State of Smart Manufacturing report. Below are a few takeaways from the report!
81% of manufacturers say external and internal pressures are accelerating digital transformation, with cloud/SaaS, AI, cybersecurity, and quality management ranking as the top areas for smart manufacturing technology investments.
95% of manufacturers have invested in or plan to invest in AI/ML over the next five years.
Organizations investing in generative and causal AI increased 12% year-over-year, signaling a maturing approach to advanced technologies beyond experimentation.
Cybersecurity ranks as the second-largest external risk, with 49% of manufacturers planning to utilize AI for cybersecurity in 2025, up from 40% in 2024.
48% of manufacturers plan to repurpose or hire additional workers as a result of their investments in smart manufacturing. Also, 41% are using AI and automation to help close their skills gaps and address labor shortages.
Quality control remains the top AI use case for the second consecutive year, with 50% of respondents planning to apply AI/ML to support product quality in 2025.
IT/OT Academy Launch [IT/OT Insider]
China’s Industrial Unprofitability Problem [Noahpinion]
Speed is Everything [Justin Lopas]
Podcast/Video:
Software Defined Manufacturing [ARC Agency]
Finance & Transactions 💵
Venture Capital:
Applied Intuition - A company that provides software solutions to help build autonomous systems for vehicles such as cars and trucks, alongside its work for the U.S. government, focusing on defense applications.
$600 million [Series F] - Led by BlackRock and Kleiner Perkins
Pelico - A Supply Chain Orchestration Platform revolutionizing complex manufacturing operations.
$40 million [Series B] - Led by General Catalyst and joined by 83North and Serena
Uncountable - A company offers a cloud-based solution purpose-built for R&D environments, enabling enterprises to unify experimental data, accelerate product development cycles, and deploy AI-driven optimization tools.
$27 million [Series A] - Led by Sageview Capital and joined by SE Ventures, Teamworthy, 8VC, and MK Capital
Senra Systems - A company that manufactures wire harnesses for the aerospace and defense (A&D) industry.
$25 million [Series A] - Led by Dylan Field and CIV and joined by General Catalyst, Sequoia Capital, Founders Fund, 16z, 8VC, and Pax
Workwhile - A company building an innovative AI-powered labor platform that matches businesses with reliable hourly workers.
$23 million [Series B] - Led by Rethink Impact and joined by Khosla Ventures and Reach Capital, Citi Impact Fund, GingerBread Capital, and Illumen Capital
Supply Wisdom - A company building a full-stack, real-time supply chain risk intelligence SaaS platform.
$14 million [Series B] - Led by Jurassic Capital.\
Lumion - A company building a platform that transforms how trade schools operate and scale.
$14 million [Seed] - Led by TTV Capital and joined by Tusk Venture Partners, CreativeCo Capital, and Nine Four Ventures
Prisma X - A company building a robotics teleoperations platform via a decentralized incentive structure.
$11 million [Seed] - Led by a16z and joined by Stanford Blockchain Builder Fund, Symbolic, Volt Capital, and Virtuals Protocol









How are they claiming that appliance in 2019 last 10+ years? I guess they mean appliances that had been in service, but it also sounds like they are predicting the future.
Also, "favoring modular, non-repairable parts" - to me this would imply the unit as a whole IS repairable by swapping out modules. Some things on a washing machine are quite easy to fix if you know what you're doing... Though I recently surrendered and purchased a new model.